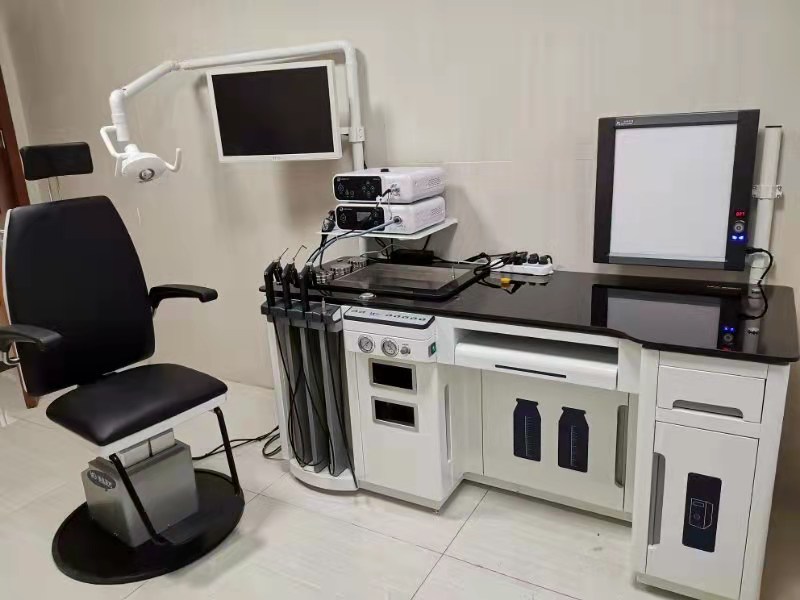
Application of electronic video laryngoscope combined with wireless endoscope in difficult airway
1.1 Study Design: Prospective, randomized paired design. 1.2 Case selection and group screening The preoperative evaluation in our hospital complies with the diagnostic criteria for difficult airways formulated by domestic experts. The general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation is planned, and the Wilson grading for laryngeal exposure using Macintosh laryngoscope after anesthesia induction is grade 3 or above. The 60 patients with the same grade were matched into pairs and randomly divided into TESL-110 electronic video laryngoscope combined with Disposcope endoscope group (T group) and Macintosh laryngoscope group (M group). 1.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria of cases 1.3.1 Inclusion criteria 1. The preoperative evaluation meets the diagnostic criteria for difficult airway established by domestic experts, that is, at least two of the following items are present: ① Modified Mallampati classification is grade III and IV; ② The distance between the upper and lower incisors (opening degree) was less than 3 cm; ③ the nail-jaw distance was less than 610 mm; 2. Wilson grade 3 and above using Macintosh laryngoscope for laryngeal exposure after induction of anesthesia. 1.3.2 Exclusion criteria: (1) Mouth opening is less than 2.0 cm; (2) Macintosh laryngoscope cannot be placed; (3) Patients with unpaired laryngeal exposure at all levels. Observation indicators Wilson grade of laryngeal exposure, intubation time (from the operator's first interdental lens insertion to the accurate placement of the tracheal tube into the trachea, excluding the time of mask-assisted breathing during multiple intubations), Success rate of first intubation, number of intubations, pharyngeal bleeding, tooth or gum damage, switching to another intubation method, or use of a laryngeal mask. 1.3.3 Wilson grading criteria for laryngeal exposure: Wilson grade 1: the entire glottis can be seen; Wilson grade 2: half of the glottis can be seen; Wilson grade 3: only spoon cartilage can be seen; Wilson grade 4: no part of the glottis can be seen , only the epiglottis can be seen; Wilson grade 5 cannot see any part of the larynx. Indirect laryngoscope laryngoscopy grading according to Wilson classification of laryngeal exposure for direct laryngoscopy. 1.4 Statistical processing SPSS 17.0 statistical software was used for analysis, measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), paired sample t test was used for comparison between groups, χ2 test was used for enumeration data comparison, and multiple correlated samples were used for grade data Friedman's test in the nonparametric test, p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. 1.5 Results of the study Compared with the Disposcope laryngoscope group (M group), the TESL-110 laryngoscope and the combined use of the TESL-110 laryngoscope (T group) showed lower grades of laryngeal exposure in the T group, pharyngeal bleeding, tooth or gingival damage, and alterations. The probability of using other intubation methods or laryngeal mask is lower, the first intubation success rate, the number of intubations are less, and the intubation time is shorter. The results showed that compared with the M group, the T group had a lower grade of laryngeal exposure, and the intubation rate was significantly higher than that of the M group, with a certain difference, p<0.05.